Polymers are increasingly being designed keeping very specific properties in mind. This often requires multi-layered polymers when multiple properties are needed in a single structure. Depending on the characteristics desired, the final structure can include anywhere from three to 11 layers.
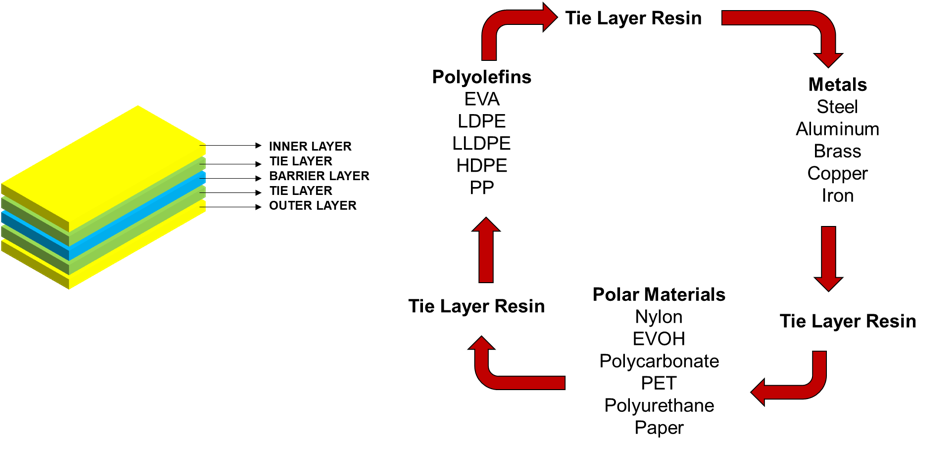
Multi-layered structures using different resins are difficult to manufacture especially when two dissimilar layers, i.e., a polar and a non-polar substrate, are involved. In such cases, tie layer resins – acid or anhydride-modified resins are used build multi-layer polymers. Exhibit 1 shows a typical tie layer graphic structure, for a three layered structure.
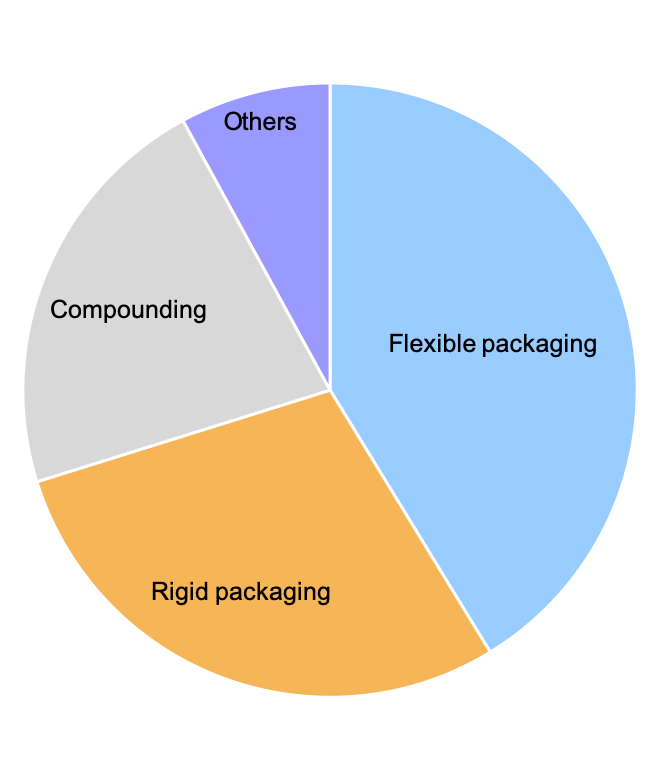
Tie layer resins were initially launched for flexible packaging applications but have now found their way into a variety of applications including rigid packaging, compounding, pipe coating, and medical devices. Exhibit 2 shows the breakdown of the North American tie layer resin market by application. Tie layer resin use is dominated by flexible packaging, followed by rigid packaging, compounding and other applications.
Flexible packaging is mainly used for food, in particular cheese and meat packaging, where properties such as moisture retention, aroma resistance, heat resistance and oxygen barrier properties are important. With rising standards of living globally, more people are looking to enhance shelf life of packaged food driving demand for tie-layer resins.
Tie layer resins are also used in rigid packaging applications such as multi-layered bottles for milk, juices, pesticides, and medicines due to key properties like flexibility, toughness, heat and cold resistance, crack resistance and barrier properties. They are also used in barrier sheets and automotive gas tanks. Their use in automotive gas tanks is driven by the need to light-weight cars for increased fuel economy.
Compounding is another application for tie-layer resins and includes wood-plastic composites, coupling agents and nylon modification. Wood-plastic composites are more resistant to decay, rot, and mold in comparison to wood. Further, they do not need to be painted and their properties can be modified for wet use. They are thus used in outdoor deck floors, furniture, fences, benches and also automotive door panels to cell phone covers. Modified nylon can be used to make puncture-resistant films, with better drawability, and low humidity content. With the growth of building and construction and automotive sectors, compounding segment is growing at an attractive pace globally.
Other applications include pipe coating, multi-layered pipe applications, and metal cladding among many others. Metal cladding makes roofing lighter, durable and more resistant than traditional roofing in buildings. Compounded pipes give the same advantages and thus this segment, also mimics the growth in building and construction sector although it has been slower due to low adoption.
ADI Chemical Market Resources has just released the 2019 global tie layer resins market assessment and forecast covering market size and segmentation by region and product type, key players and their competitive positions, growth opportunities, and strategic implications. You may download the study prospectus and contact us at info@adi-cmr.com or +1 281 506 8234 to learn more and subscribe.
By Uday Turaga and Panuswee Dwivedi

